You may be finding that your network or internet connection is slow or unreliable, you may also find that your computer responds far more slowly whilst you are using network resources because your network adapter drivers are not fully optimised. Wireless network adapter users may find that they cannot connect to some wireless points and/or that wireless range is not what they expect.
Any of these issues could be related to using outdated network adapter drivers so update them.
The primary types of network adapter that you will find in use today are PCI, PCI-Express or USB. Even wireless and cabled network adapters that are integrated into a laptop or computer will still use one of these fundamental bus types. Despite who you bought your laptop or computer from (i.e. Dell, HP, Acer, Sony) you will most likely find that a thrd party supplied the network adapter module or chip. This is actually a good thing because it means that you are not restricted to the often outdated drivers that your system manufacturer will issues when your machine is first produced but then subsequently forget about and never update.
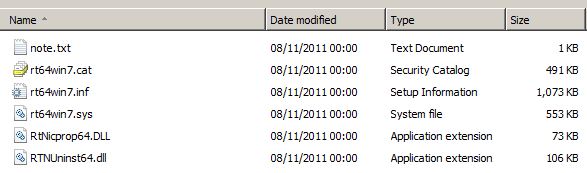
The process to update the drivers usually involves downloading and extracting the zipped/compressed driver file and then using Device Manager to verify and update the drivers are compatible and will install. You will usually find that the extracted drivers folder includes an “inf” file and various “dll” files.
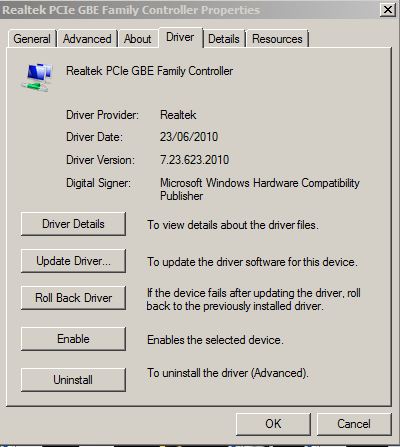
Once you have the drivers downloaded and extracted on your machine its time to launch Device Manager and find the network adapter that you wish to update the drivers for. On my example machine we want to update the Realtek PCIe Gigabit Adapter so we will double click on it and verify the current driver version.
Here we can see the driver version is “7.23.623.2010 and the date the drivers were released is “23/06/2010”.
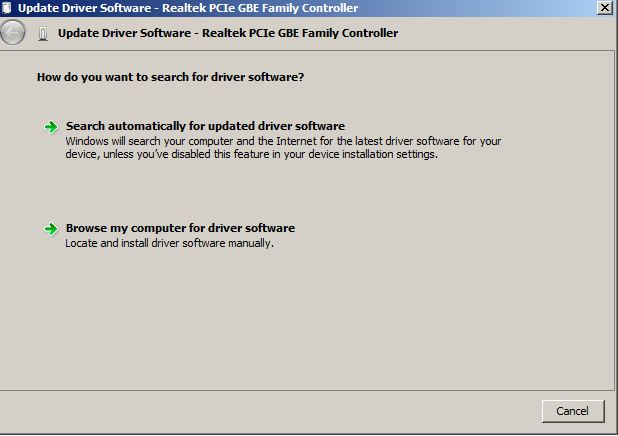
Now we want to click “Update Driver” and select the location of the new drivers that we downloaded earlier. To do this we need to click “Browse my computer for driver software” and then selecte the location of the extracted driver files.
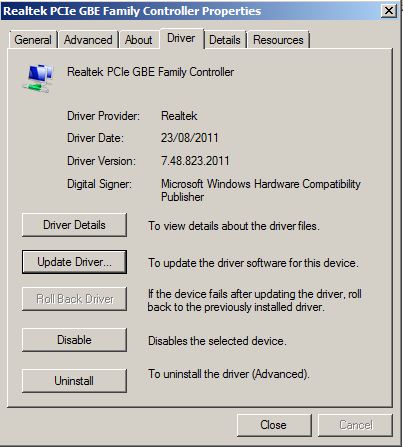
Once we have carried out the update the new version will show along with the updated driver release date.
You will usually find that the network adapter in your computer or laptop is manufactured by one of the companies listed below, next to each manufacturer is also a link to the official driver download/support page.
Intel http://downloadcenter.intel.com
Realtek http://www.realtek.com.tw/downloads/
Broadcom http://www.broadcom.com/support/ethernet_nic/downloaddrivers.php
Nvidia http://www.nvidia.co.uk/Download/index.aspx?lang=en-uk
Marvell http://www.marvell.com/support/downloads/search.do
Ralink http://www.ralinktech.com/en/04_support/support.php?sn=500
D-Link http://www.d-link.co.uk/support
Netgear http://support.netgear.com/app/
Linksys http://homesupport.cisco.com/en-eu/support/linksys
Belkin http://www.belkin.com/uk/support/